Cardiovascular Disease & Smoking
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in the US. Quitting smoking can lower your chances of having a heart attack or stroke. Learn more about cardiovascular disease and smoking.
What is cardiovascular disease?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) includes any disease of the heart and blood vessels. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease are all types of CVD.
Why should I worry about CVD?
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in the United States every year. Over 600,000 people will die because of cardiovascular disease this year.
What can CVD do to my body?
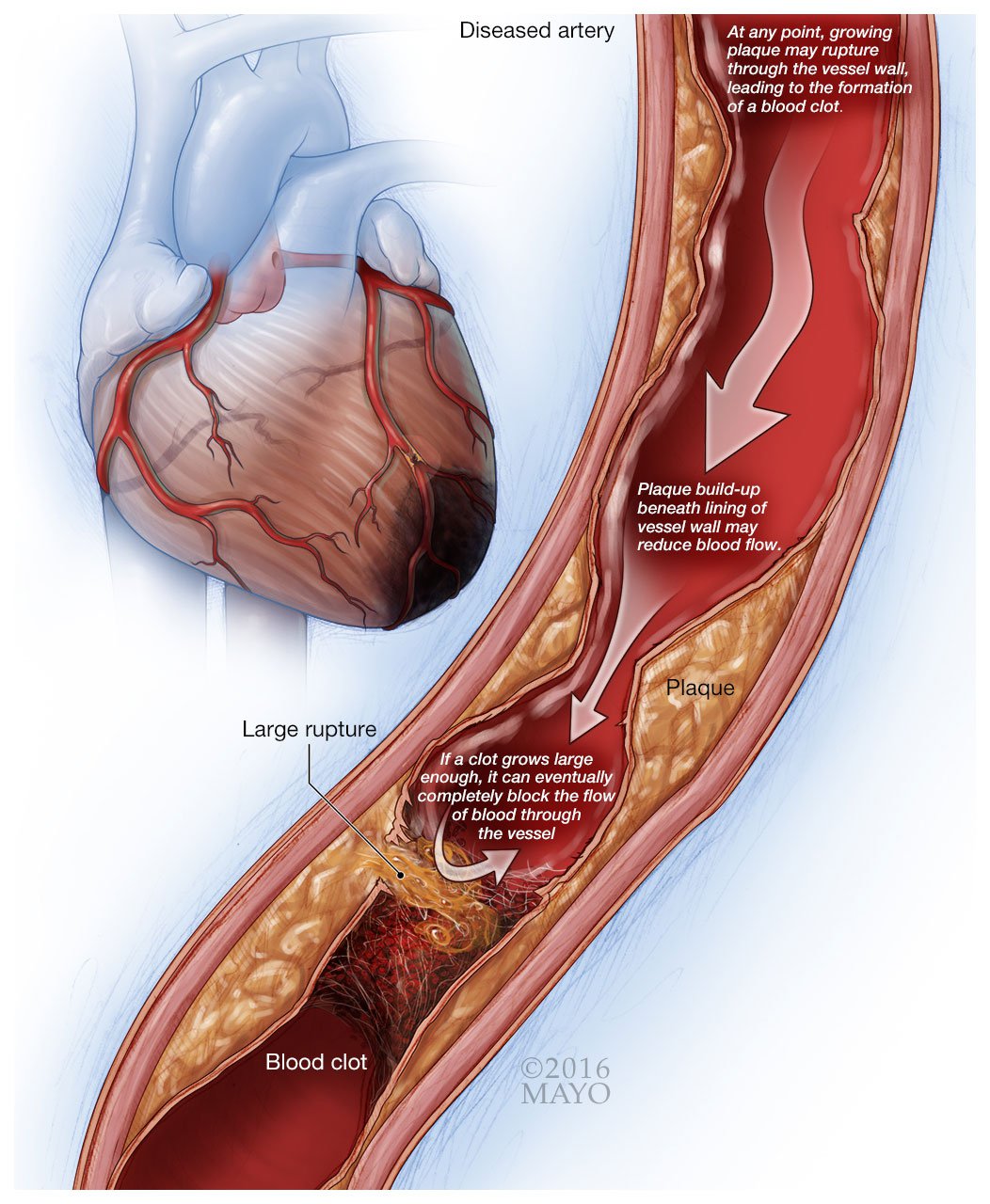
Most CVD is caused by build-up of cholesterol in blood vessels. Over time, blood vessels become more and more blocked until no blood can get through them at all. These "road blocks" in your blood vessels can cause different things to happen, depending on where they are in your body. Blockages in the blood vessels to the brain will cause stroke. Blockages in the arteries that feed the heart muscle (aka Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)) can cause a heart attack.
I don't want a heart attack! What can I do to prevent it?
The biggest risk factors for the development of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) are:
- Being older
- Being male
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Being inactive
- Strong family history of coronary artery disease
- Diabetes
- Smoking cigarettes
While most of these risk factors have to do more with your genetics, there are a few that you can do something about. Options include exercising, maintaining a healthy weight, and QUITTING SMOKING. In fact, because quitting smoking lowers your risk for CAD so fast, it is the most important thing you can do.
Here's how smoking makes CAD worse. Smoking puts carbon monoxide into your blood. This means less oxygen gets to your heart. At the same time, smoking speeds up your heart rate. This means your heart needs more oxygen. But it doesn't get it, because of the carbon monoxide already in your blood. So it beats faster to try to deliver more oxygen to your body. A faster heart beat means more heart strain over time. See the problem?
To make matters worse, smoking increases your risk of forming blood clots. So if you have CAD, and your blood vessels are already partly blocked, a blood clot can quickly and completely block an artery. Blocked artery = heart attack.
Smoking has a huge impact on build up and blockages in your blood vessels. It is possible to have surgery to repair build-up or improve circulation (such as a coronary stent or coronary bypass surgery). But smoking after surgery can wipe out any benefits!


Does smoking impact medications?
Women who take birth control pills and smoke cigarettes have a greater chance of heart attack and stroke than women who don't smoke. Women who smoke should use an alternative form of birth control, or ideally, stop smoking.
How fast will I see results related to CAD if I quit smoking?
Results will depend on how advanced your CAD is already. People with early stages of CAD should see their symptoms get better very quickly. Symptoms that improve may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness or pain with exercise or other movement
- Unusual weakness with exercise
- Leg pain with exercise
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in an arm, leg, or face
In people who stop smoking and also treat some of the other risk factors (exercise, healthy weight) blocked arteries can get better. It's almost like adding extra lanes to a small country road.
In people who have later stages of CAD and a history of heart attack, the risk of another heart attack goes way down after they quit smoking:
- After 1-2 years of quitting, the risk of another heart attack is cut by more than half.
- By 3 or 4 years after quitting, the risk of another heart attack is the same as someone who never smoked.
Quitting smoking is the most important thing to do if you have CAD and you want to lower your risk of heart attack. Not cutting down, QUITTING. Fact: even one cigarette per day can lead to CAD and a heart attack.
What if I don't smoke, but I'm around people who smoke?
Secondhand smoke increases CAD among nonsmokers.
In fact, heavy exposure to secondhand smoke is the same as smoking a half pack of cigarettes each day. There is no safe level of exposure to tobacco smoke for prevention of CAD.
So, how can I quit?
If you have CAD or another form of cardiovascular disease, quitting smoking is the most important thing you can do to lower your chances of a heart attack or stroke.
There are lots of ways to go about quitting. If you quit using the best science-based methods like those offered here on EX, you are more likely to be able to quit for good.
You have the best chance of quitting if you use medications and create a plan to change your smoking behavior. Getting support throughout your quitting journey can also improve your chance of success, whether it's from family members and friends, or the EX Community.
About Quit Smoking Medications
Will using quit smoking medications impact any of my cardiovascular disease (CVD) medications?
Quit smoking medications are safe to use with the most commonly prescribed CVD medications. If you have any questions or concerns, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or health care provider about your plans to quit smoking.
There are seven medications approved in the United States for helping people quit. Five of these are nicotine replacement products (patches, gum, lozenge, inhaler, and nasal spray). None of these medications speed up the progress of cardiovascular disease. None of them cause worsening heart problems. And they are safe for people to use who have had a recent heart attack, stent, or bypass surgery. Best of all, each of these medicines help people quit smoking.
I heard using quit-smoking medications can actually cause a heart attack or stroke. Is that true?
No. Using nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) to quit smoking will actually lower your risk of heart attack. Many studies have confirmed that using NRT is safe to use by people with heart disease.
Is it dangerous if I smoke while I use NRT?
No. There is no increased risk of heart attack or stroke if you continue to smoke while using NRT. Of course, the goal of treatment with NRT is to stop using tobacco completely. But as anyone who has tried to quit will tell you, there are times when you may slip and smoke during a quit attempt. That's OK, even if you're using NRT.
In fact, NRT can help calm withdrawal and urges to smoke for people who are trying to cut down their smoking gradually. No heart problems or increased risk of stroke was observed in studies that examined using NRT while cutting down smoking.
Does varenicline (Chantix) cause serious heart problems?
No. Varenicline is not associated with an increased risk of serious heart problems such as heart attack or heart failure. A large, recent study comparing varenicline, NRT, and bupropion (Zyban) found no increased risk of heart attack or other serious heart problems compared to placebo (sugar pill) treatment. This confirms that varenicline is safe for people with heart disease.